Country specific information – NORWAY
Printable version of this document:
![]() Vnr Country specific information of Norway
Vnr Country specific information of Norway
This document presents an overview on the handling of Vnrs (Varenummer/article number) and information carried by the Vnr in Norway. Some supplementary information on issues addressed in the common Nordic regulatory framework is also presented, mainly concerning changes to a marketed Vnr.
This document is prepared and maintained by Farmalogg AS. The Association of the Pharmaceutical Industry in Norway (LMI) is the national contracting party concerning the NNC (Nordic Number Centre, located at Pharmaceutical Information Centre Ltd (PIC) Helsinki, Finland) and the Nordic regulatory framework.
Content
- The flow of article information
- Vnr – the carrier of information
- The Changes to an Vnr introduced to the market
- Product codes in Norway
- Product groups and vnr-series in Norway
1. The flow of article information
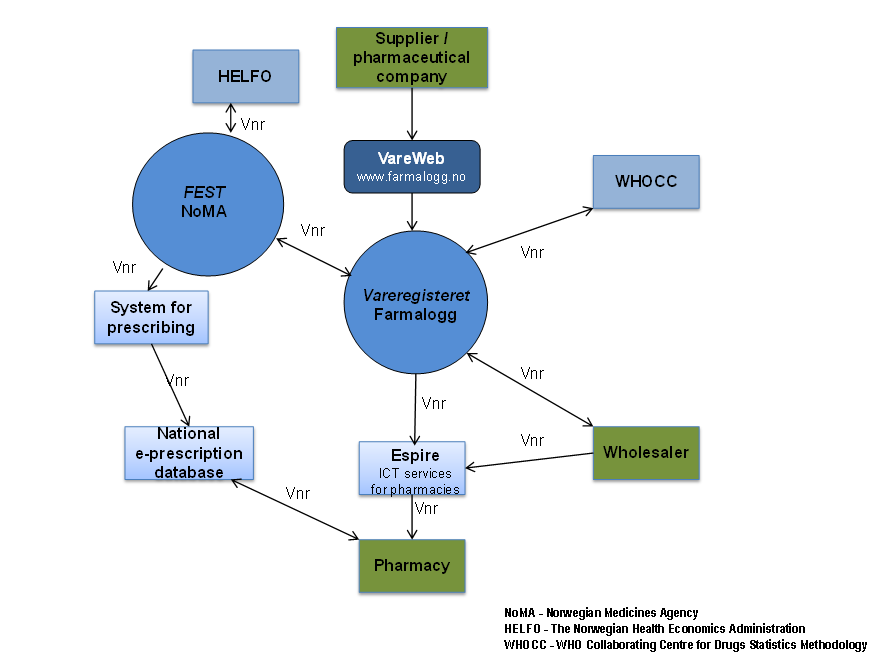
Vareregisteret is the entry point for all new products in the Norwegian market. Vareregisteret is a common, national article register for all Norwegian pharmacies and pharmaceutical wholesalers in Norway. The register includes with few exceptions all products sold through pharmacies, and contains information necessary for a safe and efficient handling and dispensing of the products from manufacturer/supplier, via wholesaler and retailer, to consumer. Vareregisteret is maintained by Farmalogg AS, a joint stock company owned by the Norwegian Pharmacy Association.
The operation of Vareregisteret is carried out by Farmalogg in cooperation with NoMA (Norwegian Medicines Agency), HELFO (The Norwegian Health Economics Administration), WHOCC (WHO Collaborating Centre for Drugs Statistics Methodology) and the pharmaceutical wholesalers. The information on the products listed in Vareregisteret is processed on data files exchanged between these partners twice a month.
FEST, maintained by NoMA, is a national database with all articles available for prescription in Norway, both first line- and specialized medicine (GPs, specialists, hospitals). FEST is available for the various systems for prescribing / EPJ (ElectronicPatientJournal). FEST is updated with information from Vareregisteret. Information from FEST, including information from the reimbursement system (HELFO), is included in Vareregisteret.
The management of the exchange of product information via FEST is essential for the coordination of information in the prescribing- and dispensing systems. This coordination is a prerequisite for the national system for electronic prescription. All information in the databases is carried by the Vnr, both the Nordic article numbers and national article numbers, as the identifier. Figure 1 gives an outline of the flow of information on medicines in Norway.
2. Vnr – the carrier of information
The information flow (fig 1) is based on the Vnr as identity and carrier of all information for prescription and dispensing in Norway. The Vnrs carry information to facilitate the handling of the products and as a structural basis for drug statistics.
The stakeholders/operators receive customized updates from Farmalogg or NoMA as they may use different information elements linked to the Vnr or in some cases add their own elements. Some information elements which are coordinated between the systems are used by most operators. Information on pricing and reimbursement provided by NoMA and HELFO is used by many operators, as information on shelf life, storage and transportation mainly concern the wholesalers. Farmalogg add different types of information to the Vnrs for specific operators, as predefined labelling choices added for the pharmacies, subcategories for statistical use in addition to the statistical information provided by WHOCC.
Regardless of type of information element, it is of paramount importance to ensure that the Vnr represents a unique identity as defined by the Nordic instructions. As the Vnrs carry information for different functions, changes must be handled with great care to avoid mix-ups.
Vnr vs. product code:
Each Vnr may be linked to multiple product codes, thereby allowing easy transfer to new product code and corresponding barcode on the packs. The barcodes are used by wholesalers and pharmacies as the identifier in the physical handling of the medicines and is essential in the verification at the point of dispensing. This means that correct product codes and corresponding barcodes are vital for correct dispensing.
3. Changes to a marketed Vnr
For the common Nordic regulatory framework on changes, see Nordic Instructions. On the topics of changes in the Nordic Instructions, please note the following elaborations:
Change of trade name
Any change of trade name should be followed by a new Vnr. Adjustments or minor changes in the name may be allowed as long as the product appears principally unchanged.
Change of package type
Change of package type, e.g. from blister to container, requires a new Vnr. For changes to package materials with no impact on pricing, the Vnr can be kept. The register distinguishes between ordinary blisterpack and unitdose blisterpacks to facilitate handling in hospitals and hospital pharmacies.
Change of prescription group for medicines with MA
When changing the prescription group from C (prescription) to F (non-prescription), a new Vnr is required. The package must be approved by the NOMA if the prescription group is to be changed from C to F.
When changing the prescription group from F to C, a new Vnr is normally required due to logistic and medicine statistic requirements. With respect to medicine statistics, it is required to differentiate between prescription and non-prescription sales.
Notification of change
The pharmaceutical company must notify Farmalogg on changes to information elements maintained by Farmalogg. A guideline on what information the company must communicate is available at farmalogg.no after logging in.
There is no link between the systems for NNC and Vareregisteret. Thus, any relevant changes concerning the Vnr must be communicated to both Farmalogg and NNC.
Please note that new Vnrs always must be registered and processed as new products in Vareregisteret. It is not possible to change the Vnr on an already marketed Vnr.
4. Product codes
Product codes must be registered on farmalogg.no, either via registration of new Vnrs, or by adding new product codes to existing Vnrs. The barcodes are used by wholesalers and pharmacies as the identifier in the physical handling of the medicines and is essential in the verification at the point of dispensing. For further information about product codes, please see the Industry standard for product codes.
Change of product code
If a GTIN is changed without a corresponding change of Vnr, the new product code must be added to the Vnr at farmalogg.no. Each Vnr may be linked to multiple product codes. For further information, see Change situations Vnr vs. GTIN. Please note the general rule; If the Vnr changes, the GTIN always changes.
5. Product groups and vnr-series in Norway
All products in Vareregisteret are grouped into 9 different product groups, and the article numbers are either Nordic article number or National article number:
| No | Product group | Article number series | Type |
| 1 | Medicines with MA (marketing authorisation) | 00 00 01 – 19 99 99 37 00 00 – |
Nordic |
| 2 | Pharmacy produced medicines | 20 00 00 – 36 99 99 |
National |
| 3 | Commodities incl. medical equipment and products approved for reimbursement by the Norwegian Health Economics | 80 00 00 – 99 99 99 |
National |
| 4 | Chemicals | 20 00 00 – 36 99 99 |
National |
| 5 | Medicinal herbs | 20 00 00 – 36 99 99 |
National |
| 6 | Unlicensed medicines / Medicines without MA (marketing authorisation) | 20 00 00 – 36 99 99 |
National |
| 7 | Homeopathic and anthroposophic medicines | 20 00 00 – 36 99 99 |
National |
| 8 | Natural remedies and herbal medicinal products incl. traditional and well-established medicinal herbs | 00 00 01 – 19 99 99 37 00 00 – |
Nordic |
| 9 | Miscellaneous incl. work rates, packaging, publications, supplies |
20 00 00 – 36 99 99 |
National |
Nordic article numbers are assigned by the Pharmaceutical information Centre for products with marketing authorisation.
National article numbers are assigned by Farmalogg. Assigned article numbers are the property of Farmalogg AS. The national article numbers are meant for use in Norway only.